FAQs
What Do Skid Marks Mean
Published: July 31, 2023
Discover the meaning behind skid marks and gain answers to general questions about this common driving phenomenon. Learn how to prevent skid marks and ensure road safety.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Under-tec.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Skid marks are often found at the scene of accidents, as evidence of vehicle movement and the dynamics of the incident. These marks can provide important clues to investigators and experts in accident reconstruction, helping them understand how the accident occurred and who may have been at fault. Whether they are faint or deep, long or short, skid marks can reveal a wealth of information about the vehicles involved, their speed, and the conditions under which the accident took place.
In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of skid marks: what they are, the different types, how they are caused, and the significance they hold in accident investigation. We will also discuss the factors that can affect skid marks and the methods used to measure and interpret them.
Understanding skid marks is crucial for accident reconstruction experts, law enforcement officials, insurance companies, and legal professionals involved in handling accident cases. By studying skid marks and their characteristics, these professionals can piece together the events leading up to an accident, assess the actions of the drivers, and determine liability.
So, let’s delve into the world of skid marks and uncover the secrets they hold in unraveling the mysteries of vehicular accidents.
What Are Skid Marks?
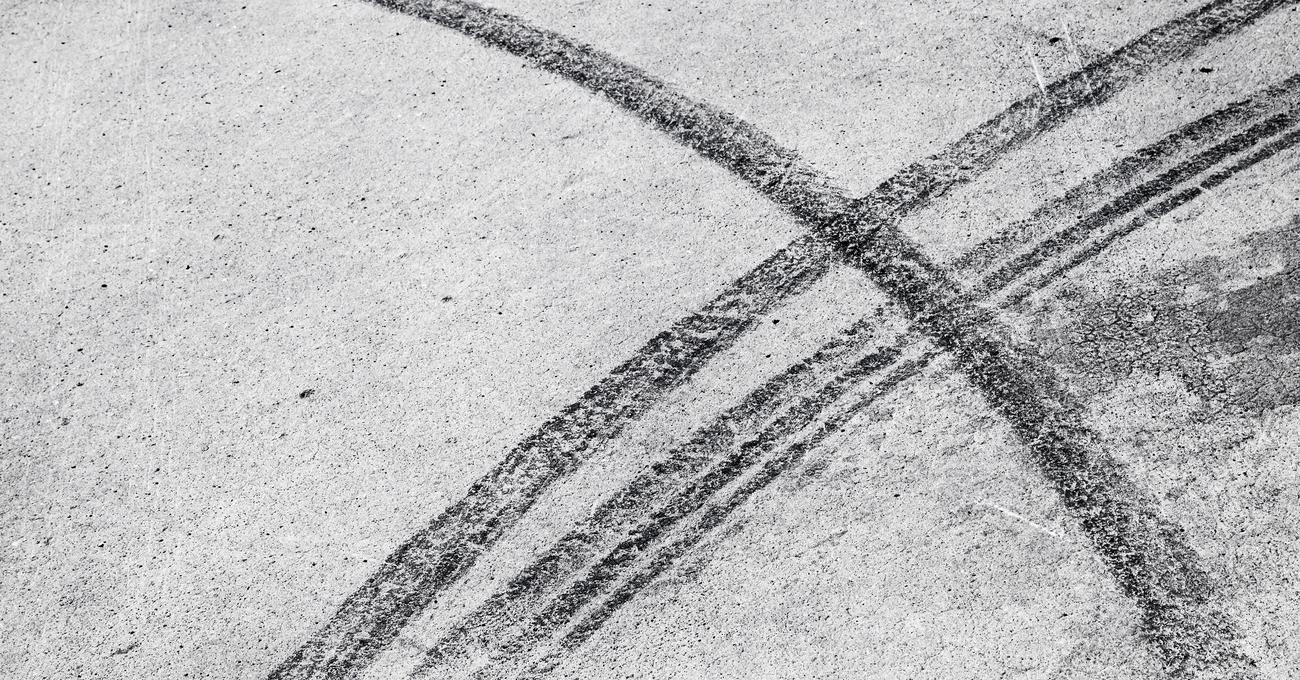
Skid marks are visible tire tracks left on the road’s surface when a vehicle’s wheels lock up and slide, instead of rotating freely. These marks are typically caused by heavy braking or sudden changes in direction, which result in a loss of traction between the tires and the road.
Skid marks can vary in appearance, depending on various factors such as the tire tread pattern, road surface, speed of the vehicle, and the force used to brake or steer. They are usually darker in color compared to the surrounding road surface, providing a visual indication of tire contact.
The length and width of skid marks can also provide valuable insights into the dynamics of the accident. Longer skid marks indicate a greater amount of time and distance over which the tires were sliding. Wider skid marks often correlate with a higher frictional force, which can indicate higher vehicle speeds or heavier braking efforts.
Furthermore, skid marks can sometimes display additional characteristics that offer further insights. For instance, a series of skid marks that show a pattern of oscillation may indicate that the vehicle was skidding sideways or undergoing a yaw motion. This information can be vital in reconstructing the sequence of events leading to an accident.
In summary, skid marks are the visible traces left by tires when there is a loss of traction between the tires and the road. Their appearance, length, width, and other characteristics can provide valuable information about the circumstances surrounding an accident, aiding professionals in deciphering the dynamics of the incident.
Causes of Skid Marks
Skid marks can be caused by a variety of factors that result in a loss of traction between the tires and the road surface. Understanding these causes is crucial in accident reconstruction, as they can provide insights into the circumstances leading to the accident. Here are some common causes of skid marks:
- Hard Braking: When a driver applies sudden and forceful pressure to the brake pedal, the tires can lock up and slide on the road surface. This can result in skid marks that are typically straight and parallel. Hard braking is often seen in emergency situations or when a driver is trying to avoid a collision.
- Excessive Speed: Driving at high speeds increases the likelihood of skidding, especially when approaching a corner or making sudden turns. The centrifugal force experienced during high-speed maneuvers can cause the tires to lose grip, leading to skid marks.
- Wet or Slippery Road Conditions: When the road surface is wet, icy, or covered in loose gravel, the tires have reduced traction, making it easier for skid marks to form. The presence of water or other substances on the road can create a barrier between the tires and the surface, causing the tires to slide and leaving behind skid marks.
- Tire Defects: Worn-out or improperly inflated tires can significantly affect a vehicle’s ability to maintain traction. Tires with low tread depth or uneven wear patterns are more prone to skidding, as they have less grip on the road surface. Tire blowouts can also cause abrupt skidding.
- Oil Spills or Road Surface Irregularities: Oil spills, leaked fluids, or debris on the road can reduce tire grip, leading to skidding. Additionally, uneven road surfaces, potholes, or loose gravel can cause tires to slide and leave behind skid marks.
It is important to note that skid marks are not always the sole result of one cause but can be influenced by a combination of factors. Accident reconstruction experts take into account all relevant factors to determine the primary cause or causes of skid marks.
By analyzing the characteristics and patterns of skid marks, investigators can gain valuable insights into the events leading up to an accident and identify the contributing factors that played a role in the loss of vehicle control.
Types of Skid Marks
Skid marks can vary in appearance and characteristics, depending on the specific circumstances of the accident. Understanding the different types of skid marks can help accident reconstruction experts piece together valuable information about the dynamics of the incident. Here are some common types of skid marks:
- Braking Skid Marks: These skid marks are the most common and occur when the vehicle’s wheels lock up due to excessive or sudden braking. They are typically straight, parallel, and uniform in width. The length of the skid marks can indicate the distance traveled while in the skid. Braking skid marks are often used to estimate the initial speed of the vehicle.
- Steering Skid Marks: Steering skid marks are produced when the driver abruptly turns the steering wheel, causing the tires to lose traction and slide sideways. These skid marks are often curved or nonlinear in shape, indicating the path the vehicle was taking during the skid. Steering skid marks can provide insights into the driver’s actions, the vehicle’s speed, and the point of impact.
- Acceleration Skid Marks: Unlike braking skid marks, acceleration skid marks occur when a driver rapidly accelerates, causing the drive wheels to lose traction and spin on the road surface. These skid marks are typically short in length and wider than braking skid marks.
- Combination Skid Marks: In some cases, multiple skid marks of different types may be present at the accident scene, indicating complex vehicle maneuvers. Combination skid marks occur when a driver is simultaneously braking, steering, or accelerating, resulting in a combination of braking, steering, or acceleration skid marks.
By analyzing the type, shape, and characteristics of skid marks, accident reconstruction experts can gain insights into the actions of the driver, the sequence of events leading up to the accident, and the forces acting on the vehicle. This information is vital in reconstructing the accident and determining liability.
Interpreting Skid Marks
Interpreting skid marks requires careful analysis of their characteristics and patterns. Accident reconstruction experts utilize various techniques and formulas to extract valuable information from skid marks. Here are some key factors considered when interpreting skid marks:
- Skid Mark Length: The length of skid marks can provide an estimation of how far a vehicle traveled while in the skid. By measuring the length of the skid marks and factoring in variables such as vehicle weight, coefficient of friction, and deceleration rate, experts can estimate the initial speed of the vehicle.
- Skid Mark Width: The width of skid marks can indicate the frictional force experienced between the tires and the road surface. Wider skid marks often indicate heavier braking efforts or higher vehicle speeds. However, the width can also be influenced by tire characteristics, road surface conditions, and other factors, so it should be evaluated in conjunction with other evidence.
- Skid Mark Direction and Shape: The direction and shape of skid marks can reveal important details about the vehicle’s maneuvers. Straight and parallel skid marks typically indicate heavy braking, while curved or nonlinear skid marks can suggest steering or yaw motions. These patterns help reconstruct the path and dynamics of the vehicle prior to the accident.
- Skid Mark Color and Depth: Skid marks are usually darker than the surrounding road surface due to the rubber material being deposited on the road. The depth of the skid marks can indicate the intensity of the skid. Deeper skid marks may suggest heavier braking or a higher frictional force. These characteristics can help determine the severity of the skid and the forces involved.
- Other Physical Evidence: Skid marks should be evaluated in conjunction with other physical evidence at the scene, such as tire scuff marks, vehicle damage, debris, and witness statements. This holistic approach helps corroborate the findings and provides a more accurate reconstruction of the accident.
Accident reconstruction experts use mathematical formulas, computer simulations, and their expertise to piece together the data gathered from skid marks and other evidence. By interpreting skid marks, they can reconstruct the sequence of events, determine vehicle speeds and movements, and establish the factors contributing to the accident.
Factors Affecting Skid Marks
Skid marks are influenced by various factors that can affect their appearance, length, and characteristics. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately interpreting skid marks and reconstructing the dynamics of an accident. Here are some key factors that can impact skid marks:
- Road Surface: The condition of the road surface significantly affects the formation and appearance of skid marks. Dry pavement provides better traction, resulting in shorter and thinner skid marks. On the other hand, wet, icy, or loose surfaces reduce tire grip and can lead to longer and wider skid marks.
- Tire Condition: The condition of the vehicle’s tires plays a vital role in skid mark formation. Tires with low tread depth or uneven wear patterns have less grip on the road, making them more prone to skidding and leaving longer skid marks. In contrast, well-maintained tires with proper inflation and good tread depth provide better traction, resulting in shorter skid marks.
- Vehicle Weight: Heavier vehicles exert more force on the tires, leading to deeper and longer skid marks. The weight distribution across the vehicle can also affect the appearance and patterns of skid marks. For example, skid marks may differ when a vehicle with an uneven weight distribution skids compared to a vehicle with a balanced weight distribution.
- Speed: The speed of the vehicle at the time of the skid directly impacts the length and appearance of the skid marks. Higher speeds result in longer skid marks, as the vehicle covers a greater distance while sliding. Additionally, higher speeds can also affect the width and depth of the skid marks due to increased tire friction and forces.
- Braking Force: The force applied to the brakes directly affects the depth and intensity of the skid marks. Heavier braking efforts lead to deeper and more pronounced skid marks, indicating a higher frictional force between the tires and the road surface. Lighter braking forces result in shallower and less defined skid marks.
These factors are interrelated, and their influence on skid marks should be considered collectively when interpreting the evidence. Accident reconstruction experts carefully analyze the location, appearance, length, and other characteristics of skid marks to assess the impact of various factors and reconstruct the events leading to an accident.
Importance of Skid Marks in Accident Reconstruction
Skid marks play a vital role in accident reconstruction by providing valuable evidence that helps experts understand how an accident occurred and determine factors such as vehicle speed, braking, and vehicle dynamics. Here are some key reasons why skid marks are essential in accident reconstruction:
- Vehicle Speed Estimation: Skid marks can be used to estimate the initial speed of a vehicle involved in an accident. By measuring the length and analyzing the characteristics of the skid marks, accident reconstruction experts can apply scientific formulas and calculations to determine the speed at which the vehicle was traveling before the skid occurred.
- Vehicle Dynamics: Skid marks provide crucial insights into the vehicle’s dynamics during the accident. The length, width, direction, and shape of the skid marks can help determine whether the vehicle was braking, steering, or accelerating at the time of the skid. This information allows experts to reconstruct the sequence of events leading to the accident and understand the actions of the driver.
- Assessment of Road Conditions: Skid marks can also reveal information about the road conditions at the time of the accident. Different types of skid marks, such as those caused by wet or slippery surfaces, can indicate hazardous road conditions that may have contributed to the accident. This information is crucial in determining liability and understanding the environmental factors involved.
- Establishing Contributing Factors: By analyzing skid marks in conjunction with other evidence, such as damage patterns, witness statements, and vehicle data recorders, accident reconstruction experts can establish the contributing factors to the accident. Skid marks can help determine if the driver was speeding, braking erratically, or taking evasive maneuvers, providing a clearer picture of what took place during the accident.
- Validation of Testimony: Skid marks can serve as objective evidence to validate or challenge witness testimonies. They provide a physical record of the vehicle’s movement and actions leading up to the accident. In cases where witness accounts may vary, skid marks can provide an unbiased reference point to support or refute their claims.
Overall, skid marks are a critical piece of evidence in accident reconstruction, enabling experts to reconstruct the events leading up to an accident, assess the actions of the drivers involved, and determine liability. By carefully analyzing and interpreting the characteristics of skid marks, accident reconstruction experts can uncover essential details that help provide a comprehensive understanding of the accident.
How to Measure Skid Marks
Accurate measurement of skid marks is crucial in accident reconstruction to gather reliable data for analysis. Here are the steps typically followed to measure skid marks:
- Identify the Start and End Points: Begin by identifying the start and end points of the skid marks. This can be done by visually inspecting the marks on the road surface and looking for any clear points where the skid marks begin or end. This can be supplemented with additional evidence, such as tire scuff marks or witness testimonies.
- Establish a Reference Point: Determine a reference point in relation to the skid marks. This can be a fixed object such as a tree, lamppost, or road sign. The reference point should be easily identifiable and accurately measured so that it can be used in subsequent calculations.
- Measure the Skid Mark Length: Using a measuring tape or laser measuring device, measure the length of the skid mark from the identified start point to the end point. Take multiple measurements along the skid mark to account for any variations or irregularities. Record the measurements accurately for further analysis.
- Assess the Surface Conditions: Evaluate the road surface conditions where the skid marks are present. Note any variations in the road’s texture, such as wet or dry patches, debris, or irregularities. This information is essential for accurately interpreting the skid marks and understanding their characteristics.
- Note Additional Characteristics: While measuring the skid marks, observe and record any additional characteristics, such as width, color, or depth. These characteristics can provide further insights into the dynamics of the accident and contribute to a more comprehensive analysis.
- Photographic Documentation: Capture detailed photographs of the skid marks, ensuring that they are properly documented from multiple angles and distances. Photographs help provide a visual record and can assist in revisiting or validating measurements during the analysis phase of accident reconstruction.
It is essential to ensure accurate and consistent measurements when measuring skid marks. Any variations or errors in measurements may lead to inaccurate results and interpretations, affecting the overall analysis of the accident reconstruction.
Accident reconstruction experts follow standardized procedures and use specialized equipment to ensure precise and reliable measurements of skid marks, ensuring that accurate data is gathered to aid in the comprehensive analysis and reconstruction of the accident.
Deciphering Skid Marks
Deciphering skid marks is a critical task in accident reconstruction, as it involves analyzing and interpreting various factors to gain insights into the dynamics of the accident. Here are some key aspects to consider when deciphering skid marks:
- Length and Initial Speed: The length of skid marks can be used to estimate the initial speed of the vehicle involved in the accident. By applying scientific formulas and considering factors such as vehicle weight, coefficient of friction, and deceleration rate, accident reconstruction experts can determine the speed at which the vehicle was traveling prior to the skid.
- Skid Mark Patterns: Analyzing the patterns of the skid marks is crucial in understanding the actions and movements of the vehicle. Straight skid marks typically indicate heavy braking, while curved or nonlinear skid marks can suggest steering or yaw motions. The shape and direction of the skid marks provide valuable insights into the path the vehicle was taking before the accident.
- Skid Mark Width and Depth: The width and depth of skid marks can offer information about the intensity of the skid. Wider and deeper skid marks indicate heavier braking efforts or higher frictional forces. The width and depth of the skid marks can also vary based on factors such as tire characteristics, road conditions, and vehicle weight.
- Road Surface Conditions: Assessing the condition of the road surface where the skid marks are present is essential. Wet or slippery surfaces, loose gravel, or oil spills can significantly affect tire grip and contribute to skid marks. It is important to consider the road surface conditions as they can provide context and explain variations in skid mark appearance and characteristics.
- Relationship with Other Evidence: Skid marks should be analyzed in conjunction with other available evidence, such as vehicle damage, witness statements, and physical marks on the road surface. This holistic approach helps establish consistency and corroborate the information obtained from skid marks.
- Computer Simulation: Accident reconstruction experts often use computer simulation software to model and simulate the skid marks. By inputting the known variables such as initial speed, road surface conditions, and vehicle characteristics, the simulation can help validate the interpretation of the skid marks and provide additional insights into the accident dynamics.
Deciphering skid marks requires expertise, experience, and attention to detail. Accident reconstruction experts rely on their comprehensive analysis of multiple factors to reconstruct the sequence of events leading to the accident and understand the actions of the driver. By carefully deciphering skid marks, they can provide crucial insights into liability, contributing factors, and the circumstances surrounding the accident.
Conclusion
Skid marks are an invaluable source of information in accident reconstruction, providing crucial details about the dynamics and events leading up to an accident. By analyzing the characteristics, patterns, and measurements of skid marks, accident reconstruction experts can estimate vehicle speed, assess braking and steering actions, determine road surface conditions, and establish contributing factors to the accident.
Understanding skid marks is essential for a comprehensive and accurate reconstruction of accidents. From deciphering the length and initial speed of the vehicle to assessing the patterns, width, and depth of the skid marks, experts can piece together the sequence of events and reconstruct the actions taken by the drivers involved.
The analysis of skid marks is a complex process that involves considering various factors, such as road surface conditions, tire condition, vehicle weight, and speed. Accident reconstruction experts employ scientific formulas, computer simulations, and their expertise to accurately interpret and decipher skid marks.
By deciphering skid marks, accident reconstruction experts contribute to the effective investigation of accidents, determination of liability, and improvement of road safety measures. Skid marks provide objective evidence that can validate or challenge witness testimonies and aid in creating a comprehensive understanding of the accident.
Accident reconstruction is a specialized field that requires a deep understanding of physics, vehicle dynamics, and investigative techniques. Skid marks serve as a crucial piece of the puzzle in accident reconstruction, providing valuable insights into the events leading up to an accident and helping experts uncover the truth behind the collision.
In conclusion, skid marks are a window into the dynamics of an accident. Through careful analysis and interpretation, skid marks reveal vital information that guides accident reconstruction experts in understanding how an accident occurred and determining the contributing factors. The study of skid marks plays a vital role in the pursuit of truth, justice, and improved road safety.